Thoracic back pain refers to discomfort in the middle segment of the spine, a crucial area that supports much of the body’s weight and facilitates numerous movements. This condition can disrupt daily life, demanding an in-depth understanding of its causes, diagnosis, and treatment. This article delves into these topics, providing a comprehensive guide to thoracic back pain.
Overview of Thoracic Back Pain
The thoracic spine, spanning from T1 to T12 vertebrae, is designed for stability, protecting the chest and serving as an anchor for the ribs. Unlike the neck and lower back, this area is less prone to injury due to its limited mobility. However, when thoracic back pain occurs, it can be a significant source of distress.
Primary Causes of Thoracic Back Pain
Thoracic back pain can stem from a variety of sources, each with its specific characteristics and treatment approaches:
- Muscle Strain and Overuse: Repetitive movements, heavy lifting, or prolonged poor posture can lead to muscle strain in the thoracic region.
- Disc Problems: Though less frequent than in other spine sections, herniated or degenerated discs can still occur in the thoracic spine.
- Osteoporosis and Fractures: The weakening of bones due to osteoporosis can result in fractures, particularly in the thoracic vertebrae.
- Arthritic Changes: Degenerative diseases like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can affect thoracic spine joints, causing pain and stiffness.
- Spinal Stenosis: This condition involves narrowing of the spinal canal, leading to nerve compression and pain.
- Deformities: Conditions such as scoliosis or kyphosis alter spinal curvature, affecting the thoracic spine.
Secondary Causes and Considerations
- Infections and Tumors: Rarely, infections like tuberculosis or the presence of tumors can lead to pain in the thoracic spine.
- Systemic Diseases: Diseases that affect the entire body, like ankylosing spondylitis, can also cause thoracic discomfort.
Diagnosing Thoracic Back Pain
Identifying the precise cause of thoracic back pain is vital for effective treatment. The diagnostic process generally involves several steps:
Patient History and Symptoms
A detailed medical history helps pinpoint the origin of the pain. Important aspects include:
- Duration and type of pain (sharp, dull, radiating)
- Activities or incidents leading to pain onset
- Accompanying symptoms such as numbness or weakness
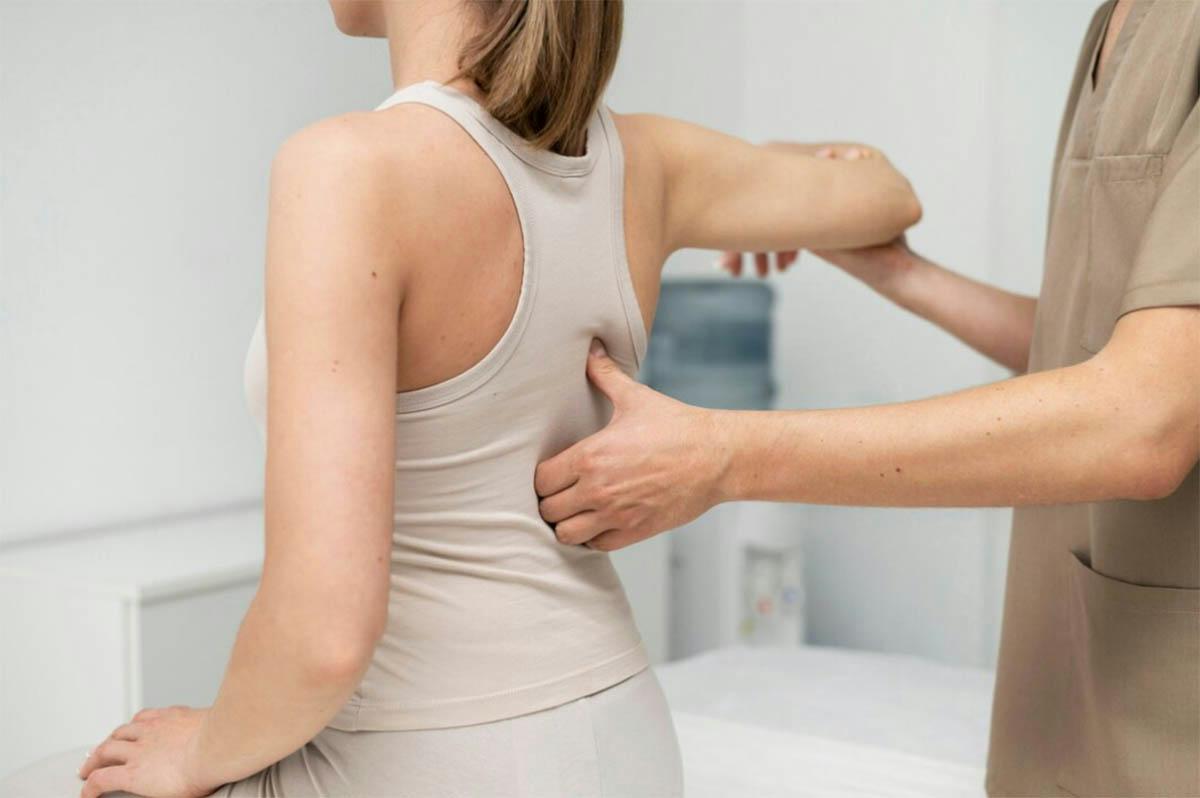
Physical Examination
A thorough physical exam can reveal much about the underlying cause:
- Inspection of posture and spine alignment
- Palpation to identify tender or painful areas
- Movement tests to assess range of motion and pain triggers
- Neurological assessments to check for nerve involvement
Advanced Diagnostic Tools
To further investigate thoracic back pain, medical professionals may employ:
- X-rays: These are fundamental for identifying fractures, arthritis, or structural anomalies.
- MRI and CT Scans: These imaging modalities provide a closer look at soft tissues, discs, and the spinal cord.
- Blood Tests: Useful in detecting infections or inflammatory markers in cases of systemic conditions.
Managing and Treating Thoracic Back Pain
The treatment plan for thoracic back pain depends on the diagnosis. Common approaches include:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches designed to strengthen muscles and improve posture.
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, and muscle relaxants can alleviate symptoms.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Changes in daily routines, ergonomic improvements, and weight management can reduce stress on the thoracic spine.
- Surgical Interventions: In severe cases, procedures to correct structural issues or relieve nerve compression may be necessary.
In summary, thoracic back pain is a multifaceted issue requiring a comprehensive approach for diagnosis and management. Understanding the diverse causes and pursuing timely medical evaluation are essential steps toward effective treatment and improved quality of life.